Areas of heavy vegetation generally have distinct
climates, which may differ considerably from climates
of nearly open areas. Falling precipitation caught in
trees before reaching the ground may be evaporated,
but precipitation, which reaches the ground, does not
evaporate or run off readily. Heavily forested areas can
absorb and store considerable quantities of water. Snow
in forests can be protected from direct insolation by the
trees and may stay on the ground for much longer
periods than snow on open, exposed surfaces. In
forests, temperature maximums and minimums are
higher than over open land at the same latitude. Relative
humidity is also higher and wind speeds are
considerably lower.
REVIEW QUESTIONS
Q6-12. Which climatic control has the biggest effect
on climatic elements?
Q6-13.
A weather station on the western coast of the
United States will receive the characteristics
of what type air as compared to a weather
station on the eastern coast?
Q6-14.
Generally, how do ocean currents effect
climate?
CLIMATOLOGICAL DATA
LEARNING OBJECTIVE: Describe the use
of climatological data in meteorology and what
references and services are available.
Climatological
records
are
based
on
the
meteorological observations that are taken at a
particular locality. This information may be presented
in a number of ways.
Temperature
records
generally
include
the
following temperature values: daily maximums and
minimums by months; the extremes; the average
temperature by year and month; the mean monthly and
annual temperature; the mean monthly maximum and
minimum temperature; and (sometimes) the monthly
and
seasonal
degree-days.
Of
great
climatic
significance is the range between the mean temperature
of the warmest month and the coldest month. Other
temperature data are sometimes given. These may
include the number of days with the following
temperatures: maximum of 90°F and above; maximum
of 32°F and below; minimum of 32°F and below; and
minimum of 0°F and below.
Precipitation records include the mean annual and
monthly totals. The range between the highest and the
lowest annual rainfall for a locality is the best indication
of the dependability of the precipitation. The records
often show the absolute maximum rainfall and snowfall
for a 24-hour period by months, as well as the
maximum and minimum precipitation for each month.
Climatic records usually show data on winds. Such
information indicates the mean hourly speed and the
prevailing direction by month. Also shown are the
speed and direction of the strongest wind for the 12
months and the year in which it occurred.
Data on cloudiness, humidity, thunderstorms, and
heavy fog are often included. Other helpful data would
be the frequency and distribution of cyclones and
anticyclones; passage of fronts; proportion of rainfall
and snowfall received from cyclonic storms and local,
air mass thunderstorms; and climatological data on
upper air conditions.
METHODS OF PRESENTATION
Climatological information is presented in many
different ways. Tables are frequently used. Maps are
particularly useful in presenting climatic information in
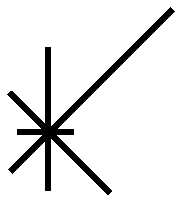
cases where geography is an important factor. Wind
data can be given by means of a device called a wind
rose, which presents information on the prevailing wind
directions. (See fig. 6-4.)
6-13
4
15
30
15
10
6
10
10
N
(NOTE : NUMBERS REPRESENT
THE % OF WINDS FROM
THAT DIRECTION DURING A
SPECIFIC TIME)
AG5f 0604
Figure 6-4.—A wind rose.