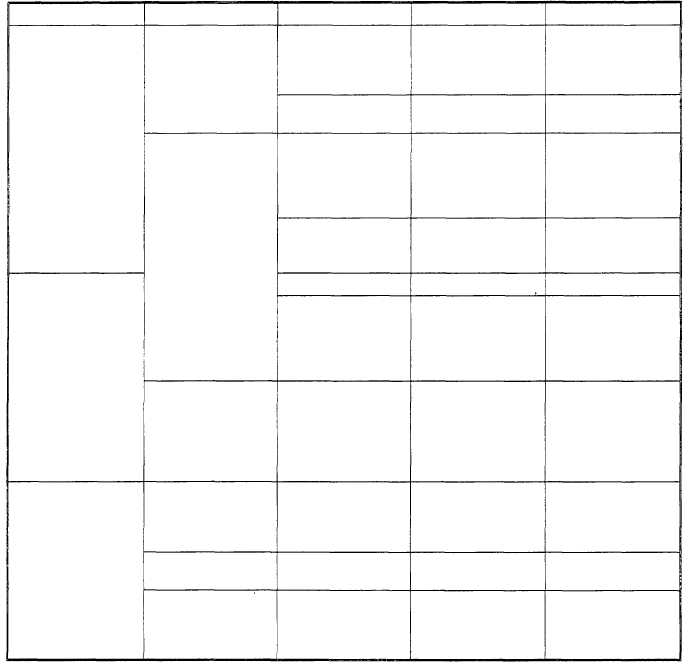
Table 1-1.—WMO Cloud Classification by Cloud Etnge, Form, Genus, Species, and Variety
ETAGE
FORM
GENUS
SPECIES
VARIETY
Cumulifrom
cumulus
humilis
mediocris
congestus
fractus
cumulonim
capillatus
bus
calvus
LOW-ETAGE
Stratiform
stratocumulus
floccus
opacus
castellanus
translucidus
stratiformis
undulatus
lenticularis
radiatus
perlucidus
stratus
nebulosus
opacus
fractus
translucidus
undulatus
nimbostratus
altostratus
opacus
translucidus
undulatus
radiatus
duplicatus
MID-ETAGE
Cumuliform
altocumulus
castellanus
opacus
floccus
translucidus
stratiformis
undulatus
lenticularis
radiatus perlucidus
duplicatus
lacunosus
Cirriform
cirrus
uncinus
radiatus
spissatus
duplicatus
floccus
intortus
castellanus
vertebratus
HIGH-ETAGE
Stratiform
cirrostratus
nebulosus
duplicatus
fibratus
Cumuliform
cirrocumulus
stratiformis
undulatus
floccus
duplicatus
castellanus
lacunosus
lenticularis
6,500 to 25,000 feet and high-etage from 20,000 to
60,000 feet).
The low-etage cloud genera may be cumuliform,
such as the cumulus or cumulonimbus (identified by
their size and extent of development); stratiform, such
as the stratus; or have mixed characteristics, such as the
stratocumulus. The mid-etage cloud genera are mostly
identified with the prefix alto. The mid-etage contains
the cumuliform clouds, such as altocumulus, and the
stratiform clouds, such as altostratus and nimbostratus.
The high-etage cloud genera contain the prefix cirro.
Cumuliform clouds in this etage are called
cirrocumulus, while stratiform clouds are called
cirrostratus. Another form of cloud found only in the
high-etage is the cirriform clouds that are the normally
thin, wispy, or hairlike ice-crystal clouds that can be
defined as neither cumuliform nor stratiform, but are
simply called cirrus clouds.
Cloud Species
Besides the identification of clouds by genera, most
cloud forms may be further identified by cloud species.
The species identifies the size, shape, or form of the
elements within a cloud layer. Table 1-1 lists the cloud
1-7