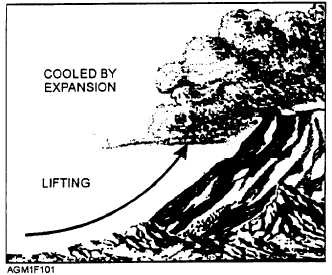
Figure 1-1.—Orographic lift.
height, but the saturated air within the cloud continues
to rise, forming the puffy, cumuliform buildups.
Stratiform clouds may form where stable air is
brought to saturation by either the addition of moisture
or by cooling the air. Most stratiform clouds, however,
form when a layer of stable air is forced upward by a
lifting mechanism. The entire layer cools as it is lifted,
reaches saturation, and forms a cloud layer.
There are four processes that cool the air by lifting
the air mass: mechanical lift, convective lift,
convergence, and vorticity.
Mechanical lift is a process by which a physical
barrier forces air aloft. The barrier may be a sloping
plain, a rising coastline, or a mountain. Those land
barriers cause a type of mechanical lift called
orographic lift (fig. 1-1). The barrier may also be air
masses of different density; for instance, when fast-
moving, warm air overrides the slower moving, cooler
air in a warm front, or when fast-moving, cold air forces
slower moving warm air aloft in a cold front. Frontal
barriers cause a type of mechanical lift known as frontal
lift (figs. 1-2 and 1-3). Turbulent lift is mechanical lift
caused by friction between the earth’s surface and the air
moving above it or between adjacent layers of air in
which wind speed (rig. 1-4) or direction is different.
Turbulent lift appears to be the key factor in the
development of cloud layers with both stratiform and
cumuliform characteristics at all levels in the
atmosphere.
Convective lift is a process that occurs when cool air
is heated from the surface and rises (fig. 1-5).
Convective lift is the key factor in cumuliform cloud
development within an air mass.
Convergence occurs when windflow at a particular
level forces air to "pile up" in a general area, which
creates a lifting action. For instance, where straight-line
winds of higher speed decrease, more air is transported
into an area than is carried away, and a mass of air builds
up vertically. This is known as speed convergence.
Alternatively, directional convergence occurs when
winds of different directions come together and merge
at a certain location. Convergence plays a key role in
cumuliform cloud development in the tropical regions.
The last lifting mechanism is vorticity. Vorticity is
the rotational motion of molecules in the atmosphere,
Figure 1-2.—Frontal lift—conditionally unstable air causing cumuliform cloud development along a cold front.
1-4