to the air mass through evaporation. Moisture may
evaporate into an air mass from precipitation falling
through the air mass and by evaporation from bodies of
water. These processes generally are only significant in
cloud and fog formation within several hundred feet of
the earth’s surface.
You will study these cloud formation mechanisms
in detail in the later training modules.
Cloud Genera
Clouds are further identified with more specific
names that are commonly referred to as cloud type, but
are more accurately termed cloud genera. The basis for
the cloud genera identification is the level at which the
cloud forms, as well as the way the cloud formed.
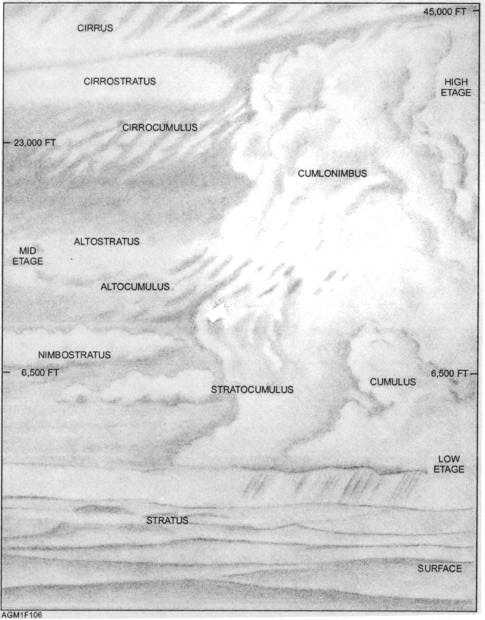
Cloud Etage
With respect to clouds, the atmosphere is broken
down into three layers or etages. In the middle latitudes
or temperate region, the low-etage is from the surface to
6,500 feet; the mid-etage, from 6,500 feet to 23,000
feet; and the high-etage, from 16,500 feet up to near
45,000 feet (fig. 1-6). The limits of the etages are
generally lower in the polar regions (mid-etage from
6,500 to 13,000 feet and high-etage from 10,000 to
25,000 feet), and higher in the tropics (mid-etage from
Figure 1-6.—Temperate Region cloud genera—cloud forms in the three etages.
1-6