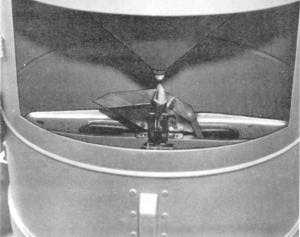
“buckets” (see figure 2-12). Each bucket automatically
dumps when filled with the equivalent of 0.01 inch of
liquid precipitation. The tipping of each bucket
activates a mercury switch, which sends a signal to the
display controller. The display controller indicates total
rainfall on the display and a “step” on the right edge of
the RD-108/UMQ-5 analog recorder chart for each
“tip” of a bucket.
The tipping buckets normally dump measured
water into a second collecting funnel. The funnel has a
drain cock at its base, which is used to drain the
collected water into a measuring cylinder. The valve is
normally left in the open position with the measuring
cylinder removed.
You should check the rain gauge frequently to
ensure that no foreign objects or dirt is clogging the
funnel or the small cuplike buckets. You should also
inspect for signs of corrosion.
So far we have discussed only some of the more
modern, high-technology electronic equipment used in
surface weather observations. Most of the equipment
discussed in the following text are not nearly as sophis-
ticated. However, much of the instruments are still
retained as back-up equipment because of their simple
design and-reliability. The instrument shelter is
surface weather observation equipment of this type.
REVIEW QUESTIONS
Q6.
What are the two major equipment groups of the
AN/GMQ-29?
Figure 2-12.—ML-588/GMQ-14 tipping-bucket rain gauge,
with the door open showing the twin tipping buckets.
Q7. What information is shown on the AN/GMQ-29
display panel?
Q8. How are sensor group inputs sent to the display
group?
INSTRUMENT SHELTER
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: State the purpose
of the ML-41 equipment shelter. Describe the
routine care required for the shelter.
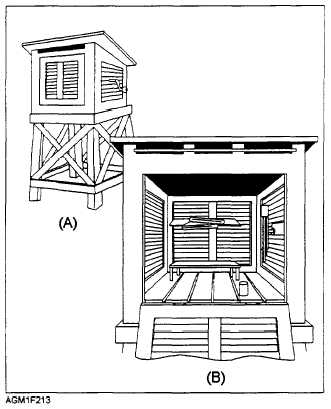
The ML-41 instrument shelter, shown in figure
2-13, is still in use at many Naval and Marine Corps
stations. The shelter is used for the protection and
acclimatization of “backup” observation equipment.
The shelter is constructed of wood, which is a poor
transmitter of heat. It has a louvered door and sides, as
well as a double-layered, sloping roof. This type of
construction helps keep out water and sunlight, yet
allows a free flow of air through the structure. These
shelters are always painted white to help reflect sunlight
and infrared radiation.
Figure 2-13.—Standard instrument shelter. (A) Construction
of support; (B) instrument arrangement inside shelter.
2-8