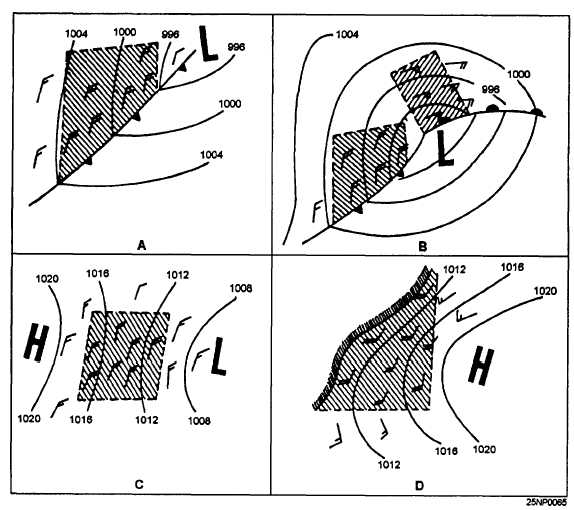
Figure 6-4.-Typical fetch areas.
Location of Fetch
bounded by coastlines, frontal zones or a change in
isobars. In cases where the curvature of the isobars is
In all cases, the first step toward a wave forecast is
large, it is a good practice to use more than one fetch
locating a fetch. A fetch is an area of the sea surface
area, as shown in figure 6-4(B).
over which a wind with a constant direction and speed
is blowing. Figure 6-4 shows some typical fetch areas.
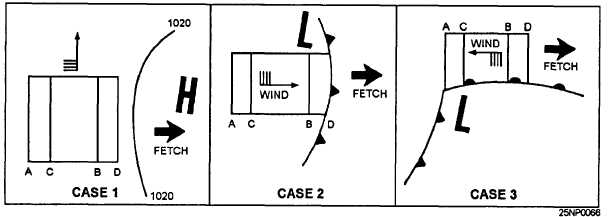
Although some semipermanent pressure systems
The ideal fetch over an open ocean is rectangular
have stationary fetch areas, and some storms may move
shaped, with winds that are constant in both speed and
in such a manner that the fetch is practically stationary,
direction. As shown in figure 6-4, most fetch areas are
there are also many moving fetch areas. Figure 6-5
Figure 6-5.-Examples of moving fetches.
6-7