stratus-type clouds with temperatures between 0°C and
minus 22°C. When formed in cumuliform-type clouds,
temperatures range from minus 9°C to minus 15°C and
are accompanied by clear icing which is then termed
mixed icing.
Glaze (Clear Icing)
Glaze is a coating of ice, generally clear and
smooth. It occurs when supercooled water droplets
deposited by rain, drizzle, fog, or condensed water
vapor strike an exposed object at temperatures at or
below freezing. Factors favoring formation of glaze are
large drop size, rapid accretion, slight supercooling,
and slow dissipation of the latent heat of fusion. Glaze
is denser, harder, and more transparent than rime and
looks similar to an ice cube. Clear icing forms on
aircraft and adds appreciably to the weight of the craft.
This additional weight has an even greater effect in
reducing the performance of the aircraft than does rime
icing. Clear icing occurs in cumuliform-type clouds at
temperatures between 0°C and a minus 9°C. It also
occurs with rime icing in cumuliform clouds at
temperatures between minus 9°C and minus 15°C.
Drifting and Blowing Snow
Drifting and blowing snow are the result of snow
particles being raised from the ground by the wind. To
classify wind-driven snow as drifting snow, the
particles will only be lifted to shallow heights (less than
6 feet) and the horizontal visibility will remain at 7
miles or more at eye level (6 feet). When the wind
drives snow to levels 6 feet or higher and the visibility is
restricted to 6 miles or less, it is classified as blowing
snow.
Spray and Blowing Spray
Spray and blowing spray occurs when the wind is
of such force that it lifts water droplets from the water
surface (normally the wave crests) and carries them into
the air. To be classified as spray, the wind-driven water
droplets will not obstruct visibility at eye level (6 feet
on shore and generally 33 feet at sea). Blowing spray
occurs when the water droplets are lifted in such
quantities that they reduce visibility to 6 miles or less at
eye level.
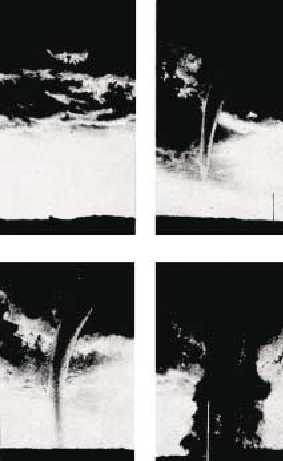
TORNADOES
A tornado is an extremely violent whirling storm
with a small diameter, usually a quarter of a mile or
less. The length of the track of a tornado on the ground
may be from a few hundred feet to 300 miles; the
average is less than 25 miles. When not touching the
ground, it is termed a funnel cloud or tuba. The
velocities of tornado winds are in the general range of
125 to 250 knots. A large reduction of pressure in the
center due to the spiraling of the air seems to cause
buildings in the path of the storm to explode. The speed
of the storm over Earth’s surface is comparatively
slow—usually 22 to 34 knots.
Most of the tornadoes in the United States occur in
the late spring and early summer in middle and late
afternoon, and they are associated with thunderstorm
activity and heavy rain. Tornadoes occur on all
continents but are most common in Australia and the
United States. They can occur throughout the year and
at any time of day. Tornadoes have been observed with
various synoptic situations but are usually associated
with overrunning cold air. Statistics show that the
majority of tornadoes appear about 75 to 180 miles
ahead of a cold front along the prefrontal squall line.
Figure 5-6 shows the various stages of development of a
tornado.
5-11
AG5f0506
A
B
C
D
Figure 5-6.—Stages of development of a tornado.