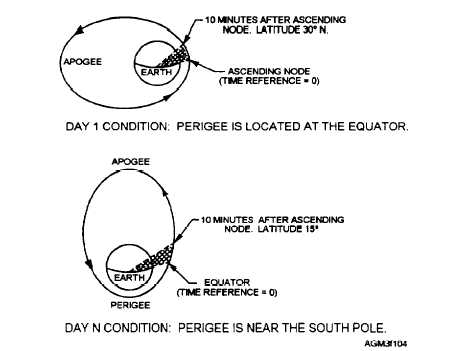
perigee, satellites move faster. When at apogee,
satellites travel slower. This change in velocity
complicates tracking of polar-orbiting satellites. For
convenience and ease of orbit calculations, time is
referenced to zero when a polar-orbiting satellite
passes the equator northbound, and increases through a
complete orbital period.
Figure 1-4 illustrates the
changes that can occur in the perigee and apogee of a
satellite over time.
Most polar-orbiting satellites also have anomalies
in their orbits. An anomaly in an orbit is any change or
deviation from a perfectly stable orbit. Some
anomalies are planned into an orbit so that the orbit
will remain sun synchronous as earth revolves around
the sun during the course of a year. Anomalies further
complicate satellite orbital predictions.
REVIEW QUESTIONS
Q1. A satellite with an equatorial orbit would have
an inclination angle of how many degrees?
Q2. What term is used for a satellite with an
equatorial orbit moving with the same speed and
direction as the earth?
Q3. What term is used to describe the period of time
when a polar orbiting satellite is traveling south
to north?
Q4. What is meant by the term "sun-synchronous"
satellite?
Q5.
Q6.
If a satellite has an ascending node time of 1400
local, what would be the approximate
descending node time at the same location?
What are the major factors that would cause
changes in a satellites apogee and/or perigee
position?
TYPES OF ENVIRONMENTAL
SATELLITES
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: Recognize the
various functions performed by environmental
satellites. Identify the major satellite programs
operated in the United States. Identify specific
types of geostationary satellites, polar-orbiting
satellites, DMSP satellites, and foreign
satellites. Recognize the advantages and
disadvantages of geostationary and polar-
orbiting satellites.
The first meteorological satellite was launched in
April of 1960, and was known as TIROS-1 (Television
and InfraRed Observation Satellite). Since that time,
numerous satellites with more advanced technology
have been introduced, and today there are many
different designs of meteorological and oceanographic
satellites. Most of these satellites have a variety of
sensor packages that survey electromagnetic energy at
several different wavelengths.
Figure 1-4.—Typical elliptical satellite orbit and changes in the orbital shape over a period of time.
1-4