APPLICATION
The EMCON planner can use PV to assess the
relative vulnerability of the various emitters on a
platform versus their value in surveillance or
communication.
The object is to minimize the
platform’s vulnerability to counterdetection.
LIMITATIONS AND ASSUMPTIONS
The restrictions as well as the principles taken for
granted in listing the PV program areas follows:
. Make sure the environment selected from the
refractivity data set is indicative of the location and time
of interest. PV is range- and time-independent.
. The maximum intercept range output is limited
to 1000 km (541 nmi). The atmosphere is usually not
horizontally homogeneous over these great distances.
. PV doesn’t account for absorption of EM energy,
In general, the absorption of EM energy by things such
as oxygen, water vapor, fog, rain, or snow adds little to
the propagation loss. Refraction is considered the main
factor in transmission.
l PV is valid for frequencies between 100 MHz
and 20 GHz.
. Sea-reflected interference is also considered only
if the receiver or emitter is below 100 m.
l The effects of a surface-based duct are
considered to dominate any contributions from the
evaporation duct.
l PV assumes the emitters are radiating at peak
power.
. The probability of detection associated with the
output ranges depends upon the probability of detection
associated with the receiver sensitivities.
. If you are attempting to verify ESM intercept
ranges achieved by your own receiver, remember that
PV outputs maximum intercept range. If a platform’s
emitters aren’t turned on at that range, there will be
nothing to intercept.
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
PV computes the maximum ESMR of an emitter.
ESMR is computed only if the emitter’s frequency falls
within one of the frequency bands of the receiver.
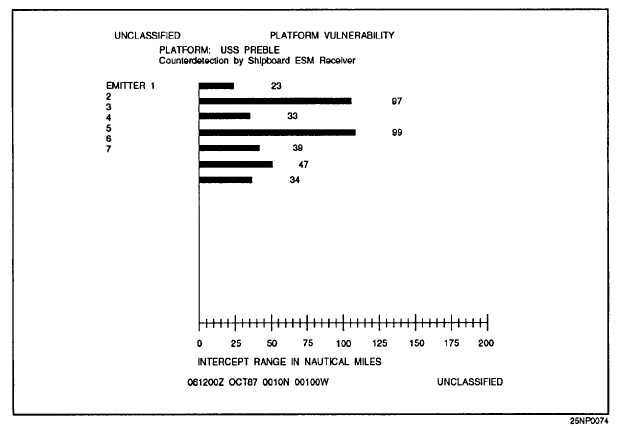
Table 7-3 shows an example output of the PV
program. The bar graph shows the maximum range that
Table 7-3.-Example Output of the PV Program
7-9